Insurance plays a critical role in financial planning and risk management. Whether you’re buying auto insurance, home insurance, health coverage, or a business policy, the process can feel confusing without expert guidance. That’s where insurance agencies come in.
An insurance agency serves as a bridge between insurance providers (carriers) and consumers, helping individuals and businesses find the most appropriate and cost-effective insurance solutions. They do far more than just sell policies — they assess risk, offer expert advice, manage claims, and provide long-term support.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore:
- What insurance agencies are
- The different types of insurance agencies
- What services they provide
- How they differ from brokers and direct insurers
- Why working with an insurance agency might be right for you
Key Takeaways
- An insurance agency helps consumers and businesses find, purchase, and manage insurance policies.
- Agencies offer expert advice, policy comparisons, and claims support.
- There are two types: captive (one insurer) and independent (multiple insurers).
- Using an agency can save time, money, and stress.
- Always verify an agency’s licensing, reputation, and range of products before partnering.
Introduction to Insurance Agencies
An insurance agency is a company or organization that sells, solicits, or negotiates insurance policies on behalf of insurance carriers (also called insurers). They work with customers to help them understand their insurance needs and find policies that fit their financial and personal risk profiles.
Agencies may be small, local businesses or large national organizations with dozens or hundreds of agents. Some work with multiple insurance companies, while others represent only one.
An insurance agency is a business entity or organization that acts as an intermediary between insurance carriers (the companies that create and underwrite insurance policies) and the consumers (individuals, families, or businesses) who need coverage.
Rather than going directly to the insurance company, most people purchase insurance through an agency. Agencies can be small, locally owned shops with just one or two agents or massive regional and national firms employing thousands of agents.
The core function of an insurance agency is to help clients find appropriate insurance coverage for their personal or professional needs, often by:
- Assessing risk
- Comparing products
- Advising on coverage
- Handling the purchase process
- Assisting with claims
- Supporting long-term policy management
Types of Insurance Agencies
Understanding the different types of insurance agencies is essential for anyone seeking the right insurance partner. The structure and business model of an agency directly impact the range of products they offer, their ability to compare policies, the level of personalization they provide, and ultimately how well they serve your specific insurance needs.
In the world of insurance, not all agencies are created equal. Broadly speaking, there are three primary categories of insurance agencies:
- Captive Insurance Agencies
- Independent Insurance Agencies
- Direct Writers / Exclusive Agencies
Let’s break down each of these types, their features, pros and cons, and which might be best for your situation.
Captive Insurance Agencies
A captive insurance agency represents a single insurance company and sells only that insurer’s products. These agencies operate under a contract with the insurer and are often branded with the company’s name and logo.
How It Works:
Captive agents are essentially employees or closely affiliated agents of the insurance company they represent (e.g., State Farm, Allstate, Farmers, American Family).
- They receive training directly from the insurer.
- They follow company policies and guidelines.
- Their ability to offer alternative pricing or products is limited to what the company provides.
Pros of Captive Agencies:
- Strong product knowledge: Since they only sell one brand, captive agents often have in-depth expertise on that company’s products and procedures.
- Brand trust and consistency: Clients may feel more confident working with a well-known brand name.
- Streamlined service: Support, underwriting, and claims processes are often highly standardized and centralized.
Cons of Captive Agencies:
- Limited options: They can only offer policies from one company, which might not always be the most competitive.
- Less flexibility: If your needs change or if your risk profile doesn’t fit the insurer’s appetite, you may be out of luck.
- Potential for bias: Recommendations may be influenced by the need to sell only in-house products.
Best For:
People who trust a specific insurance brand and value simplicity and consistency over choice and customization.
Independent Insurance Agencies
Independent agencies work with multiple insurance companies and offer a wider selection of policy options. They are free to compare different carriers and present you with the most suitable and cost-effective policy based on your individual needs.
These agencies are often local or regional and may represent a dozen or more insurers, including names like Travelers, Progressive, Safeco, Liberty Mutual, The Hartford, and niche carriers for specific risks.
How It Works:
Independent agents act on behalf of the customer, not the insurance company. They maintain contracts with various carriers and can submit your information to several insurers to get competitive quotes.
- They help tailor policies across multiple companies.
- They can switch your carrier over time if your needs change.
- They often build long-term relationships with clients.
Pros of Independent Agencies:
- More choices: You get access to multiple insurers, increasing the chance of finding better rates or coverage.
- Personalized service: Agents tailor recommendations based on your unique needs, not just what one company offers.
- Long-term support: They can re-shop your policy across carriers if rates increase or your needs change.
- Advocacy: Since they’re not tied to one brand, their loyalty is more likely to lie with the client.
Cons of Independent Agencies:
- Inconsistent experiences: Service quality and expertise can vary widely depending on the agency.
- Complexity: With multiple insurers, paperwork and processes may not be as streamlined.
- Less brand familiarity: Independent agencies may offer lesser-known carriers, which could be a downside for brand-conscious consumers.
Best For:
People who value choice, customization, and long-term flexibility. Ideal for those with complex needs (multiple cars, high-value homes, business operations, etc.).
Direct Writers / Exclusive Agencies
Direct writers or exclusive agencies are a hybrid model where the insurance company sells policies directly to consumers via their own salaried agents, call centers, or websites — without involving third-party agencies.
These may include companies like GEICO, USAA, and Lemonade, where customers often go online or call a centralized service line to get coverage.
How It Works:
Direct writers use their own staff (not contractors or agency owners) to sell insurance policies. They do not involve middlemen or local offices.
- Policies are generally standardized and priced competitively.
- Technology plays a key role — much of the service is digital or over the phone.
- Customer service is centralized and may involve chatbots or virtual agents.
Pros of Direct Writers:
- Low premiums: Cutting out the “middleman” can lower overhead costs and lead to competitive pricing.
- Convenience: Fast quotes and digital-first experience appeal to tech-savvy customers.
- Consistency: Policies, support, and claims are handled uniformly.
Cons of Direct Writers:
- Less personalized service: Customers may not have a dedicated agent.
- Limited advice: Customer service reps may not provide tailored recommendations.
- No cross-carrier comparison: You only see what one company offers.
Best For:
Tech-savvy individuals who are comfortable shopping for insurance online and prefer quick, affordable policies over detailed consultation.
Comparison Table: Types of Insurance Agencies
| Feature | Captive Agency | Independent Agency | Direct Writer / Exclusive |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insurer Representation | One insurer | Multiple insurers | One insurer (in-house staff) |
| Customer Focus | Insurer | Client | Insurer |
| Range of Options | Limited | Wide | Limited |
| Support Model | In-person or phone | Personalized, ongoing | Mostly online or phone |
| Pricing | Standard | Competitive (varies) | Often lower (low overhead) |
| Service Style | Brand-aligned | Client-first | Tech-driven, efficient |
| Best For | Loyal brand customers | Clients seeking choice | Price-sensitive, tech users |
Which Type of Insurance Agency Should You Choose?
Your ideal agency type depends on your personal situation, preferences, and level of comfort with insurance concepts:
- If you want simplicity and brand loyalty, a captive agency might be ideal.
- If you seek choice, customization, and personal advice, go with an independent agency.
- If you prioritize speed, low prices, and digital convenience, consider a direct writer or exclusive agency.
For many consumers, starting with an independent agency gives the most flexibility — especially when dealing with multiple policies or complex needs.
What Insurance Agencies Actually Do
Here’s a breakdown of what an insurance agency typically does:
Needs Assessment
- Conduct a thorough assessment of the client’s assets, risks, budget, and legal obligations.
- Help determine the type and amount of insurance needed (e.g., liability, property, health, life).
Policy Shopping
- Compare quotes and policy terms from different insurers (especially for independent agencies).
- Identify coverage that balances cost and risk.
Customer Education
- Explain complex terms, coverage limits, exclusions, and optional endorsements in plain language.
- Educate clients on what each policy covers — and what it doesn’t.
Policy Issuance and Maintenance
- Facilitate the purchase of policies.
- Handle renewals, endorsements, cancellations, and updates to personal information.
Claims Support
- Guide policyholders through the claims process.
- Help clients gather documentation and communicate with adjusters.
Ongoing Risk Management
- Conduct periodic reviews of coverage needs.
- Recommend policy changes as life events or business risks evolve.
Services Provided by Insurance Agencies
Insurance agencies often provide a wide variety of services, including:
- Personal Insurance Services: Homeowners, renters, auto, life, and health insurance.
- Commercial Insurance Services: Business liability, commercial auto, workers’ comp, property, cyber liability.
- Specialty Insurance: Boat, RV, travel, umbrella policies.
- Employee Benefits: Group health, dental, and disability insurance.
Some agencies also offer financial services such as retirement planning, annuities, or investment products.
How Insurance Agents Get Paid
Understanding how insurance agents are compensated is important for transparency.
- Commissions: Most agents earn a percentage of the policy’s premium (typically 10-20%).
- Renewal Commissions: Agents often receive smaller commissions for policy renewals.
- Fees: In some cases, agencies may charge service fees — particularly for business or specialty lines.
- Bonuses & Incentives: Insurers may reward agents for meeting sales targets or maintaining low claim ratios.
Insurance Agency vs. Insurance Broker
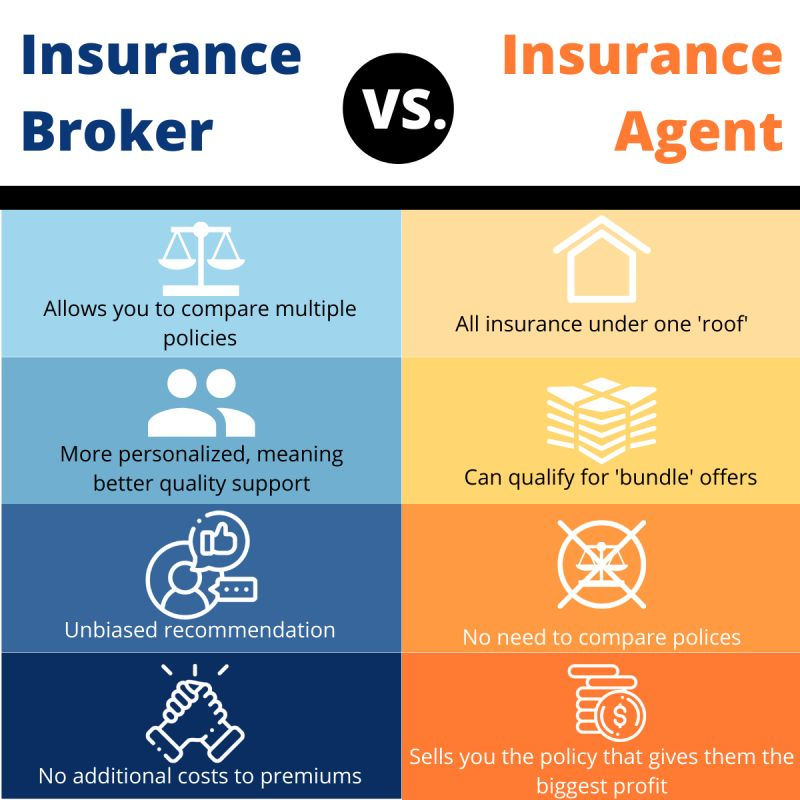
While the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, there are differences.
When it comes to buying insurance, two types of professionals often come up: insurance agencies and insurance brokers. To the average consumer, these terms may seem interchangeable, but they represent two distinct roles in the insurance industry. Understanding the differences between an insurance agency and an insurance broker is crucial for making informed decisions about your coverage, costs, and customer experience.
In this section, we will explore:
- Definitions and roles
- Key responsibilities
- How they get paid
- Who they represent
- Pros and cons of working with each
- Real-world examples
- Which one might be best for your situation
Let’s break it down.
What Is an Insurance Agency?
An insurance agency is a business that sells insurance policies on behalf of one or more insurance companies (insurers). The agency’s job is to help you find, purchase, and manage a policy that suits your needs.
There are two main types of agencies:
- Captive Agencies – represent only one insurer
- Independent Agencies – represent multiple insurers
Insurance agents working within an agency are licensed professionals authorized to bind coverage, provide quotes, and assist with claims. While agents offer advice and support, they usually do so within the framework of the insurers they represent.
What Is an Insurance Broker?
An insurance broker is a licensed professional who represents the buyer (client), not the insurance company. Brokers work independently of insurers and are legally obligated to act in the best interest of the client.
Unlike agents, brokers don’t bind coverage directly. Instead, they:
- Assess the client’s risks
- Recommend policies
- Shop for the best terms across the market
- Act as advocates in complex claims or renewals
- Negotiate terms with insurers on behalf of the client
Brokers may work with many different insurance companies, often including specialty carriers not available through standard agencies.
Benefits of Using an Insurance Agency
Using an agency offers several advantages:
- Expert Advice: Agents are trained professionals with deep knowledge of insurance.
- Time-Saving: Agencies do the shopping and paperwork for you.
- Advocacy: They advocate on your behalf during claims.
- Tailored Coverage: Get policies that reflect your unique needs.
- Customer Service: Ongoing support and relationship-based service.
How to Choose the Right Insurance Agency
When selecting an agency, consider the following:
- Reputation and Reviews: Check Google, Yelp, Better Business Bureau.
- Licensing: Ensure agents are licensed in your state.
- Range of Products: More insurers = more options.
- Customer Service: Responsive and attentive agencies offer better support.
- Specialization: Choose an agency with expertise in your area (e.g., small business, personal lines, high-risk).
The Role of Technology in Modern Insurance Agencies
Today’s agencies are becoming increasingly tech-savvy:
- Digital Quote Tools: Instant rate comparisons.
- Customer Portals: Online access to policies and payments.
- AI Chatbots: 24/7 support.
- CRM Tools: Help agents provide more personalized service.
Tech-enabled agencies are often faster and more efficient.
Common Myths About Insurance Agencies
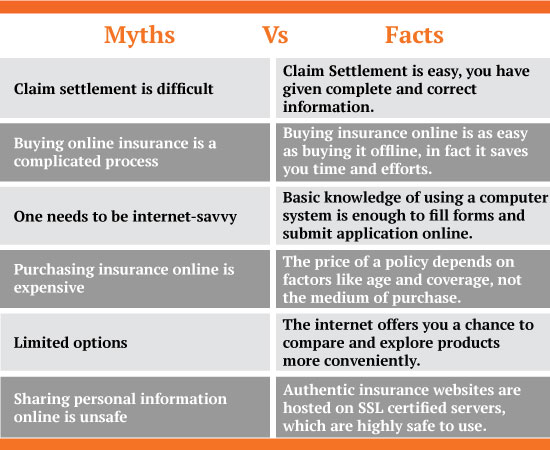
Insurance agents are biased toward their commission
Fact: Ethical agents are trained to act in your best interest and offer solutions that meet your needs.
Agencies are only for rich people
Fact: Insurance agencies serve everyone, from renters to million-dollar homeowners.
You pay more using an agency
Fact: In many cases, agencies help you save money by finding discounts or better policies.
Real-Life Scenarios: How Agencies Help
Homeowner Files a Fire Claim
An agent helps submit documentation, speaks to adjusters, and ensures the client gets a fair payout.
Business Owner Needs Cyber Liability
A commercial lines specialist at the agency explains risks and provides tailored quotes.
Family Moves to a New State
The agency helps transfer coverage, update auto insurance, and re-assess liability limits.
Industry Regulations and Compliance
Insurance agencies are regulated at the state level. Key regulatory elements include:
- Licensing Requirements: Agents must pass exams and maintain continuing education.
- Ethical Standards: Agencies must act fairly and in accordance with legal obligations.
- Data Privacy Laws: Agencies must protect your sensitive data.
Also Read: How Can I Get the Best Home Insurance Rates?
Conclusion
Insurance is not just a legal requirement — it’s a strategic tool for protecting your life, family, business, and assets. Working with an insurance agency simplifies the complex world of insurance by providing guidance, comparison, support, and peace of mind.
Whether you’re a first-time homeowner, a seasoned business owner, or someone looking to optimize existing policies, partnering with a trusted insurance agency ensures you have the protection you need, when you need it — without overpaying or being underinsured.
FAQs
1. Do I pay more by buying insurance through an agency?
No. Agencies are compensated by the insurer, and in many cases, they help you save money.
2. Can an insurance agency cancel my policy?
No. Only the insurance carrier can cancel a policy, but the agency may assist you in reinstating it or finding alternatives.
3. Is it better to use a local agency or a national one?
It depends. Local agencies may offer personalized service, while national agencies may offer broader options and technology.
4. Can agencies help during the claims process?
Yes. Many agencies act as your advocate during claims and help expedite the process.
5. Do all insurance agencies offer the same policies?
No. Each agency works with different insurers and may have access to unique products.
6. How do I know if an agency is trustworthy?
Look for licensing, reviews, industry affiliations, and ask for references if needed.
7. Can I switch agencies without losing my policy?
Yes. You can often switch agents within the same insurer or move your policy to a new agency.


